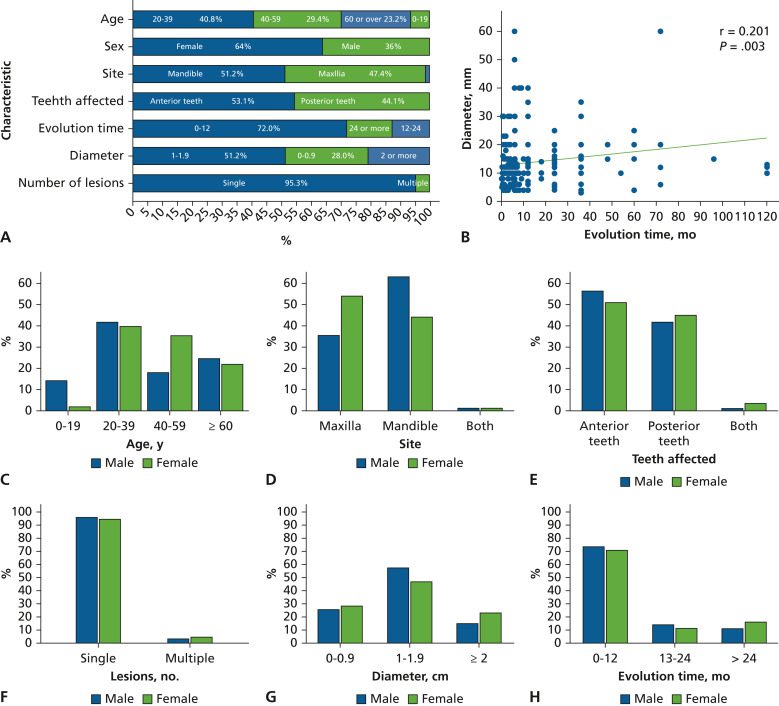
Background
The association between clinicopathologic characteristics and the relapse of fibrous
gingival hyperplasia is unknown.
Methods
The records of 211 consecutive patients with a clinicopathologic diagnosis of fibrous
gingival hyperplasia were retrieved. Patients who experienced relapse after surgical
excision of the lesion were considered case patients (n = 30). All control patients
were informed that there was no recurrence (n = 181). Logistic regression was used
to evaluate the associations among different characteristics and the recurrence. Stratified
analyses on sex was applied to identify the different associations.
Results
Binary logistic regression showed that patients with ulcer (odds ratio [OR], 3.23;
95% CI, 1.18 to 8.83) or mechanical stimulation (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.03 to 5.68) had
a higher risk of experiencing recurrence. Stratified analysis of sex identified significant
association in females (ulcer: OR, 4.04; 95% CI, 1.14 to 14.34; mechanical stimulation:
OR, 3.30; 95% CI, 1.15 to 9.42). No significant difference was observed in males (ulcer:
OR, 2.44; 95% CI, 0.40 to 15.06; mechanical stimulation: OR, 1.62; 95% CI, 0.28 to
9.40). Male patients with larger epulides had fewer recurrence (OR, 0.13; 95% CI,
0.02 to 0.74). There was no significant difference in pathologic calcification between
case and control patients (P > .05).
Conclusions
Patients with ulcer and mechanical stimulation may have a high risk of experiencing
recurrent epulis.
Practical Implications
More attention should be paid to patients with ulcer and mechanical stimulation. Apart
from complete surgical removal, it is important to remove local stimulation to prevent
recurrence of these lesions.