General characteristic of the research
Actuality of the research
Carious lesion of deciduous (primary) teeth in children is widespread (E.M. Kuzmina, 1995; Lukinykh L. M. et al., 2001; I.V. Afonina, 2005; S. N. Kiwanukai et al., 2004; B.L. Edelstein, 2005; Mahejabeen R. et al., 2006 ). Progression of deciduous (primary) teeth carious lesion rate in infancy and preschool age (E.E. Maslak et al., 1998; Frias-Bulhosa and joint authors, 2002; Lee M., Sissons S.N., 2003 ) is registered in many countries throughout the world. Difficulty in treatment of caries in deciduous (primary) teeth is due to not only anatomico-physiological characteristics of primary teeth and oral cavity of a child but difficulty in management strategies in young children (V.V. Korchagina, 2005). It predisposes to the development of carious complications and premature primary teeth extraction, which in its turn, produces a negative effect on permanent teeth germs, systemic child health condition, leads to the development of odontogenic inflammatory maxillofacial diseases and dentofacial anomalies in children (Vinogradova T.F., 1987; Yelizarova V.M. et al., 1998; Dmitriyenko S.V. et al., 1999; Sayfullina Kh.M., 2001; Schechter N., 2000; Welbury R.R et al. 2005). That’s why, the problem of childhood caries treatment is considered to be the most significant and actual one in dentistry.
To overcome own children’s and parents’ fear to dental care is one of the most serious problem (Luneva N.A., 2001; Kent G., 1985; Lindsay S., Jackson S., 1993 ). As a sound of a working dental drilling machine is one of the powerful factors in dentophobia development (Mikhaylova M.A., 2006), so great attention is paid to designing noiseless “friendly” carious treatment techniques, especially for children (Pakhomov G.N., Leontyev V.K., 2004; Mount G.J., 2002; Frencken J.E., Holmgren C.J., 2004). However, many current carious treatment techniques (ozonotherapy, preparation with a jet device, laser or ultrasound) proved to be less acceptable for young children. Other techniques have some particular disadvantages and do not always lead to good results. So, applying a silver method dyes carious tooth tissues into black, so in principle many parents reject it. On the other hand, a silver method results in a great number of complications (E.E. Maslak et al., 2000 ).
Atraumatic restorative treatment of dental caries and chemical mechanical preparation of carious cavities (Lysenkova I.I., 2004; Kleymenova O.A., 2005; Schriks M.S., van Amerongen W.E., 2003; N. Lopez et al., 2005) have proved to be more promising techniques for pediatric dentistry. There is not enough evidence concerning application of these techniques for dental caries treatment to children’s primary teeth in literature, the influence of various carious preparation techniques on children’s behavior modification in oral cavity sanation has been poorly studied, indications and contraindications for their use are not clearly identified.
In deep caries management it is suggested to use a protective calcium liner or carry out deep fluoridation of the pulp floor (Kuryakina N.V., 2001; Zolotova L.Yu., Korshunov A.P., 2005; Knappwost A., 1995, 2000, 2001; Maltz M. et al., 2001 ). However, these techniques are rarely used in primary teeth, as it is considered that “there is no deep caries in primary teeth”. On the other hand, hard tissues of primary teeth have specific anatomico-physiological characteristics, promoting a high infectious process distribution, development of complications in small carious cavities (M.S. Duggal et al., 1999, 2004). That’s why, median caries treatment is to protect the pulp and foster mineralization of dentin affected by caries. From this point of view a deep fluoridation of dentin before median caries treatment is perspective, but clinical efficacy of this technique in median caries treatment of primary teeth has not been studied yet. Glass ionomer restorations are used as tooth-colored filling materials for primary teeth (I.N. Kuzmina, 2001; Tran L.A., Messer B.L., 2003; Wang L. et al., 2004; Burke F. J. T. et al., 2005). In recent years a possibility of esthetic restoration of caries in primary teeth with light – cured filling materials in children has been under study (Mass Ye. et al., 1999, Fuks A., 2000). However, there is no evidence in need for esthetic restoration of caries in primary teeth in literature reviews; also there are insufficient data on comparison characteristics of different median caries treatment techniques for primary teeth.
The object of the research
justification of comprehensive therapy in the course of median caries treatment of primary teeth to enhance effectiveness of treatment for children aged 1-5.
The following tasks have been outlined
1. to assess children’s behavior aged 1-5 in the process of oral cavity sanation applying various carious cavity preparation techniques
2. to compare quality of various carious cavity preparation techniques in children aged 1-5
3. to determine effects of deep fluoridation of the pulp floor on enhancing clinical effectiveness of caries treatment of primary teeth in children
4. to clarify children’s needs aged 1-5 for esthetic restoration against caries in primary teeth and to estimate results of esthetic light- cured filling material use in median caries treatment of primary teeth
5. to work out a comprehensive median caries treatment technique for primary teeth and evaluate effectiveness of its use in children aged 1-5
Scientific newness of the research
Children’s behavior in oral cavity sanation subject to application of various carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth has been studied for the first time. It is proved that atraumatic restorative treatment of dental caries and chemical mechanical preparation of carious cavities improve children’s behavior, but the use of a dental drilling machine contributes to the development of negative attitude to teeth treatment.
A comparative study of various carious cavity preparation techniques (conventional, atraumatic, chemical mechanical) using caries – detector on primary teeth in children aged 1-5 has never been conducted before. The use of caries –detector is considered medically necessary for the purpose of assessing a complete removal of carious dentine in all studied preparation techniques. Indications for the use of various preparation techniques in treatment of caries in primary teeth in children aged 1-5 have been worked out.
Deep fluoridation of the pulp floor before filling has been applied for median caries treatment of primary teeth in children firstly and high clinical effectiveness of this method has been established.
Children’s need for esthetic restoration of caries in primary teeth was ascertained. Clinical effectiveness of median caries treatment of primary teeth with the use of light- cured filling material in children, which corresponded to the results of using glass ionomer chemical curing cement, was determined.
A comprehensive schedule of caries treatment of primary teeth was designed and approbated, its high clinical effectiveness -94,8 % was ascertained in comparison with conventional treatment method (effectiveness- 83,5%) in children aged 1-5.
Scientific theoretical significance of the research
Theoretical significance of the research consists in obtaining new data on comparative efficacy of different carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth in children, effect of a preparation technique on children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation, children’s need for esthetic treatment, significance of deep fluoridation to enhance a particularly beneficial effect on median caries treatment of primary teeth in children.
Practical significance of the research consists in designing a comprehensive schedule of caries treatment of primary teeth in children; its use has considerably enhanced effectiveness of treatment.
On the base of obtained data indications for the use of various preparation techniques in treatment of median caries in primary teeth has been presented. The necessity to use caries –detector has been proved for evaluation of preparation technique quality. Resources to use esthetic fillings for primary teeth have been determined.
Theses to be substantiated
1. Children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation is improved subject to application of atraumatic restorative treatment of dental caries and chemical mechanical reparation of carious cavities. Use of conventional preparation by means of a dental drilling machine contributes to the development of negative attitude to dental treatment.
2. Use of caries –detector is considered medically necessary for the purpose of assessment a complete removal of infected tissues and promotes preparation quality in all studied preparation techniques.
3. Deep fluoridation of the dentin floor enhances effectiveness of caries treatment in primary teeth in children.
4. Comprehensive schedule enhances effectiveness of median caries treatment of primary teeth in children aged 1-5 in comparison with conventional treatment.
Approbation of the research results. Implantation of findings . Publications on the thesis.
Materials of the research were presented and discussed in: conferences of young researchers of VolSMU (2004-2006), XI regional conference of young researchers in Volgograd region (Volgograd,2005), VI international scientific conference “Health and education in III millennium”(Volgograd, 2005).
The research was approbated at a chair meeting of pediatric, therapeutic, surgical dentistry, propaedeutics, prosthodontics and refresher training chair of Volgograd State Medical University (September, 2006).
Implantation of findings is due to a practical work of a dentist in a dental clinic of VolSMU, municipal health care institution “Children’s (pediatric) clinical dental polyclinic № 2” and municipal health care institution “Children’s dental polyclinic № 5” in Volgograd, being used in the process of education at the chair of pediatric dentistry at Volgograd State Medical University during lectures and practical classes for students, interns and residents, and at courses of refresher training.
Materials of the research are presented in 8 publications, 3 of them are in central press.
Thesis frame is due to logic of the study and delivered aims. The thesis consists of introduction, literature review, description of the objective and methods of the research, the chapter of own investigation, conclusion, summary, practical recommendations, list of literature, including 194titles (69-russian, 125- foreign). It is presented on 127 pages containing 7 tables and 17 figures.
The objective and methods of the research
According to the aim and tasks of the research a multistage research was set up, in which 448 children aged 1-5 were recruited. Children were evenly sampled within strata of sex and age.
Research basis
municipal health care institution “Children’s clinical dental polyclinic № 2” in Volgograd. Participation in the study was voluntarily. Informed consent on children’s participation in a conducted study was received from parents. Test protocols were confirmed by regional Ethics Committee.
The first stage included the study of parents’ attitude (192 families) towards different carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth and children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation. In the process of carrying out the oral cavity sanation, children’s behavior depending upon the use of different carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth was assessed. 47 children underwent the oral cavity sanation with the use of a conventional preparation of carious cavities in their primary teeth, 48 children were performed an atraumatic preparation and 97 children – a chemical mechanical reparation. Conventional preparation of carious cavities in primary teeth in children was performed with the use of a dental drilling machine, high-speed and low-speed headpieces, diamond dental drills, hard-alloy dental drills and steel burs. Atraumatic method of carious cavity preparation of primary teeth was performed due to ART methodology (Pakhomov G.N., Leontyev V.K., 2004). Chemical mechanical method of carious cavity preparation of primary teeth was performed with “Carisolv”, “Medteam”, Switzerland. Glass ionomer cement was used for a tooth filling. Children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation was recorded during their first four visits.
Performance measurement of parents in the area of pediatric oral health was the following: 1) satisfaction with the experience care by children, complete agreement with a doctor in all questions (in a manner consistent with the parents’ and child’s psychology needs); 2) dissatisfaction with the method of treatment chosen by a doctor for some reasons, (unmet treatment need in children) necessity to change it.
Children’s behavior was assessed on the base of three criteria: 1) good: a child is sociable, confides in his doctor, sits well and opens his mouth; 2) satisfactory: a child is not easy- going, sits badly and opens his mouth badly, parent’s and paramedical personnel assistance is required to provide comprehensive treatment.
The second stage included the study of the qualitative assessment of different carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth in median caries with caries- detector in 53 children. Conventional preparation technique was applied to 30 carious cavities, atraumatic technique – to 15, chemical mechanical – to 62. To evaluate the quality of carious cavity preparation of primary teeth a caries –detector: “Color-test” (“VladMeVa”) was applied. On the base of analysis of received data indications to use different carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth in case of median caries treatment in children were identified.
The third stage of the research presented the results of the study of deep fluoridation of the pulp floor in78 children in the course of median caries treatment in children (145teeth), when compared with conventional treatment (215 teeth). Deep dentin fluoridation of the pulp floor was performed with “dentin bonding agent” (dentin sealant liquid), “Humanchemie”, Germany.
During the fourth stage parents’ attitude to esthetic treatment of primary teeth in children (according to questionnaire data of 100 respondents) was ascertained and effectiveness of median caries treatment of 56 primary teeth in 23 children aged 3-5 with the use of different carious cavity preparation techniques and further restoration with light-cured filling material “Vitremer TM”, “3M ESPE” was established. Conventional preparation technique was performed in10 teeth, atraumatic – in 13, chemical mechanical – in 33.
During the fifth stage, on the base of conducted surveys, a comprehensive median caries treatment schedule for children with primary teeth aged 1-5 was developed. Comprehensive treatment included: sparing preparation of carious cavities (ART, CMP methods); use of caries- detector to control the quality of a carious cavity preparation; deep fluoridation of the pulp floor after preparation; carious cavity filling with glass ionomer cement. A comprehensive schedule was applied to381 teeth in 142 children. Conventional treatment of median caries (preparation with a dental drilling machine, GIC (glass ionomer cement) filling) was performed in the same group of children in 315 teeth. Carious lesions’ location, depending on a method of median caries treatment of primary teeth, was approximately equal. In 18 months effectiveness of comprehensive median caries treatment of primary teeth in comparison with conventional treatment was established.
To evaluate results of median caries treatment of primary teeth in children the following parameters were considered: presence or absence of complications after treatment (pulpitis or periodontitis) and secondary decay, quality of fillings related to anatomic shape, dental surface health, and gingival attachment. According to the results of children’s examination the quality of median caries treatment of primary teeth was evaluated by means of two measurements: 1) positive result: filling is conserved, restoring the anatomical dental form, preserving gingival attachment or there is a small defect not involving the dentin, there are no signs of secondary decay or carious complications; 2) negative result: extensive filling decay, gingival attachment defect, involving dentin, irregular surface with pronounced pits, fissures, splits, partial filling breakage, falling out of filling (wear), recurrent caries and caries complications development.
All statistical data processing were conducted with a computer IBM AT Pentium-4, using a statistical mathematical software package (Microsoft excel 2000). Marginal category (%), mean error amount (m), significance test (t), and credibility value of diversity (p) were identified. Diversity is considered to be statistically reliable in t> 2; p<0, 05.
Results of own investigations
Parents’ attitude and children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation. The results of interview showed that most parents met the oral health needs of children covered by a doctor and had positive attitude to any provided oral health care. Only 4,2% of parents were not satisfied with the experience of care by their child.
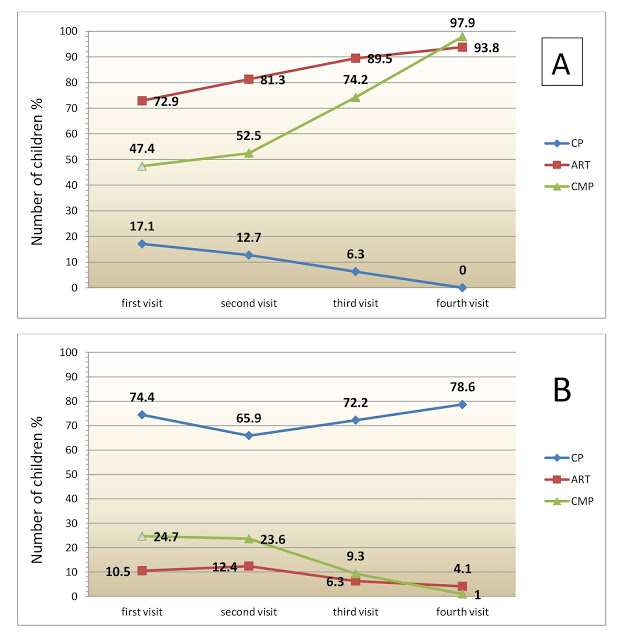
Children’s behavior varied in the process of oral cavity sanation. In the group of conventional preparation most (74, 4%) children showed a negative attitude to dental treatment during a first dental visit, their behavior was poor. In the process of oral cavity sanation with a dental drilling machine a number of well-behaved children increased and to the fourth visit amounted to 78,6%. At the same time a number of well-behaved children decreased: during the second visit- up to 12, 7%, during the third visit – up to 6, 3 %. During the fourth visit there was no one with good behavior. Satisfactory behavior was recorded in 21, 4% of children in conventional carious cavity preparation.
Most (72, 9%) children showed good behavior when used ART method on their first visit. Gradually, the number of well-behaved children increased and amounted to 93, 8% on their fourth visit. The number of children with satisfactory behavior amounted to 16, 6% on their first visit, then it had reduced to 2,1 % by their fourth visit. Bad behavior was observed in 10, 5% of children on their first visit, reduction of frequency of negative attitude in children’s towards treatment began only with the third visit and by the fourth visit had amounted to 4,1%.
Good behavior-47,4% was observed in a group of children who were performed a chemical mechanical carious cavity preparation in most cases on their first visit, its frequency increased from visit to visit 52, 5%, 74,2%, 97, 9% in compliance with the second, third, fourth visits. The number of children with satisfactory behavior amounted to 27,8 % on the first visit, then gradually decreased and amounted to 1,0% during the fourth visit. Also the number of children with poor behavior reduced from 24,7% during the first visit to 1,0% during the fourth visit.
Comparative analysis of results showed, that children met sparing preparation methods (ART and CMP) much better than preparation with a dental drilling machine (pic.1). In the process of oral cavity sanation with the use of sparing preparation methods practically all children demonstrated good behavior and positive attitude to dental treatment, but in conventional preparation opposing tendency was observed: the number of well-behaved children had reduced to zero by sanation termination, but poor behavior and negative attitude of children to treatment were kept at high level during the whole course of sanation -74,4 % -78,6% cases.

Quality assessment of various carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth. Use of caries – detector revealed remained infected dentin in all applied carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth in children. Though more often preparation defects were revealed reliably (р < 0,001) by conventional preparation technique (66,7%) that was 2,8 times greater than in CP, 5 times greater than in ART (pic.2). Statistic reliability of diversity (13,3±8,8% and 24,2± 5,4 % respectively, р < 0,05) was not found out between preparations results by ART and CMP methods. It should be noted, that in carious cavity preparation more successful removal of infected tissues was revealed after chemical mechanical preparation technique.

Thus, caries-detector use allows improving the quality of carious cavity preparation and therefore enhancing the effectiveness of caries treatment in children.
Summing up the use of various carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth in children peculiarities of conducting different procedures, advantages and disadvantages of their use were determined. Quick removal of infected tissues could be considered as an advantage of a conventional preparation technique. Use of a dental drilling machine leads to the development of a negative attitude to a dental treatment and increases the level of dentophobia in population and is the most essential disadvantage. ART method has significant advantages due to its quietness, tenderness elimination, risk minimization of accidental tooth cavity opening and damage of surrounding tissues, fear and anxiety reduction in children and parents. At the same time this technique is applied only to “opened cavities”; doesn’t always allow removing tertiary dentin; tenderness may appear in excavation of infected dentin near the horn of the pulp and along the dentin enamel junction; it requires more time for preparation itself.
Advantages of CMP are: painlessness and quietness, comfort enhancement to children and parents, safety for tunica mucosa of mouth; maximal preserving health tooth tissues; easy removal of affected tissues after their softening with gel, possibility of manual tooth tissues broadening of enamel margins, providing good cavity and butt access. Disadvantages of CMP are considered to be the following: it was not always possible to open the cavity with hand instruments, softening gel isn’t always effective in extraction of dens tertiary dentin, manual carious dentin removal on medial tooth wall of carious cavities in primary molars was ineffective; some children mentioned unpleasant drug odor; time for extraction of affected dentin had extended.
Results of deep dentin fluoridation of the pulp floor before filling with GIC in median caries treatment of primary teeth appeared to be highly effective (pic.3). Positive results after using deep fluoridation occurred reliably more often, then in conventional treatment: 94,5± 1,9% and 82,8± 2,6% respectively, р < 0,001. Negative results after using deep fluoridation occurred reliably 4,2 times more seldom then in an experimental group 5,5± 1,9% and 17,2± 2,6% and respectively, р < 0,001.

Nevertheless, it should be pointed out, that the use of deep fluoridation was effective in median caries treatment of primary teeth and Class II and V cavities, but improvement of results in Class II and III cavities was less pronounced.
The problem of esthetic fillings of primary teeth in case of caries. Results of parents’ attitude to the oral appearance of the child’s teeth showed that the majority of respondents (73,0%) considered esthetic treatment of primary teeth necessary. Only17% of respondents benefited esthetic treatment of primary teeth, 10% found difficulty in replying. At the same time choosing an appropriate method of treatment, only 33% of families could make their own decision, 60% relied on their doctor, 7% found difficulty in replying. Less (21%) families could choose a filling material themselves. On the other hand, deciding on treatment method and filling materials was limited by household income level. In spite of that 80% of families had satisfactory and good household income level; most of them preferred free medical service (17%) or cheap caries treatment of primary teeth of children (49%). Only 34% of respondents accepted esthetic teeth treatment of children.
Knowledge of light- cured material use in primary teeth in children has presented some difficulties: work “in four hands” is required; timetable for filling extends; a child should sit quietly for some time, following doctor’s orders properly and rapidly; appropriate isolation of working area from oral fluid is necessary. According to it, filling was difficult to perform in younger children under age 3, in less sociable children, in active and curious children who are not able to sit with their open mouth for a long time.
Repeated examination of children in 12 months revealed that number of satisfactory results of Vitremer use after CMP was 87,8%, after ART -84,6%, after CP-80,0% , number of negative results – 12,2%, 15,3%, 20, 0% respectively. However, diversities detected were not statistically reliable (р > 0,05). On average, use of Vitremer was effective only in 85, 7% cases. Negative results comprised 14,3% of cases, the main problem was falling out of fillings, that could be explained by difficulty in following work technique with light – cured materials in younger children.
Results of light – cured material use for primary teeth filling in median caries corresponded to the results of GIC filling (number of positive results 85,7% and 83,5% respectively, р > 0,05). On the one hand, use of esthetic light – cured materials is restricted due to low esthetic parents’ needs and their limited paying capacity, on the other hand, complexity of work and difficulties connected with children’s behavior while filling a tooth.
Comprehensive treatment of median caries in primary teeth in children.
A comprehensive treatment schedule of median caries in primary teeth in children including CMP and ART techniques, using of caries –detector to evaluate prepared carious cavities’ “rate”, application of sealants to the pulp floor and carious cavity filling with GIC was established basing on the results of the presented investigations.
After providing comprehensive treatment for median caries in primary teeth in children positive results were revealed in 18 months in 94,8% of cases, after providing conventional treatment – in 83,5% of cases (р < 0,001). Negative results after providing comprehensive treatment for median caries occurred reliably 3,2 times less than after providing conventional treatment -5,2% and16,5% and respectively, р< 0,001. It should be pointed out, that after providing comprehensive treatment for median caries in children negative results are associated with falling out of fillings (wear), there were no caries complications “under the filling”, secondary caries did not develop, but after conventional treatment these complications were registered along with others.
Results of median caries treatment of primary teeth in children depended on carious cavity localization (pic 4).

Number of negative results providing comprehensive treatment in Class I cavities (according to Black) was reliably 8,5 times less than after providing conventional treatment (1,1±0,8% and 9,3± 2,3%, р < 0,01), in Class II cavities- 1,5 times less(16,3±5,3% and 24,4± 6,7%, р > 0,05), in Class III cavities – 1,9 times less(17,9±6,1% and 34,0± 6,7%, р > 0,05), in Class IV cavities – 6,2 times less (2,6±1,5% and 16,1± 4,7%, р < 0,01). Thereby, high effectiveness of median caries treatment of primary teeth in children aged 1-5 has been ascertained by the results of comprehensive treatment, that permits to recommend applying a comprehensive schedule into dental pediatric practice widely.
Conclusions
1. Children’s behavior in the process of oral cavity sanation depends on carious cavity preparation techniques for primary teeth: use of sparing preparation techniques (ART, CMP) results in children’s positive attitude development in 93,8% -97,9% of cases; in conventional preparation in 78,6% of children negative attitude towards teeth treatment is observed.
2. Quality of carious cavity preparation of primarily teeth detected by carious – detector is better in use of sparing preparation techniques (ART, MCP) than in conventional preparation. Preparation defects have been defined in conventional method reliably (р < 0,001) 2, 8 less than in chemical mechanic preparation, and 5 times less, then in atraumatic preparation.
3. Deep dentin fluoridation of the pulp floor after preparation increases the effectiveness of median caries treatment of primary teeth in children. Number of negative results after deep fluoridation has reduced reliably in 4,2 times, in comparison with conventional treatment method: 5,5±1,9% and 17,2± 2,6% respectively, р < 0,001.
4. Need in esthetic caries treatment of primary teeth in children aged 1-5 constitutes 34%. Effectiveness of light – cured preparation material “Vitremer” use corresponds to 85,5 % of negative results – 14,3%, that is equal to the results from glass ionomer cement filling.
5. Comprehensive treatment schedule of median caries in primary teeth has been established including sparing preparation techniques (ART, CMP), using of caries –detector in the process of preparation, deep dentin fluoridation of the pulp floor and filling with GIC. Providing a comprehensive treatment schedule for median caries treatment in children aged 1-5 reliably has enhanced effectiveness of treatment in 11,3 % in comparison with conventional treatment: 94,8% and 83,5 % respectively, р < 0,001.
Practical recommendations
1. In children aged 1-5 in the process of oral cavity sanation a carious cavity preparation in case of median caries should be performed by sparing techniques:
– ART technique is recommended for active and capricious infants under age 3, in preschool children with high level of fear and anxiety in presence of good access to carious cavity;
– CMP technique is recommended for infants under age 3; any age children during their first visit to enter into good relations; patient who are afraid of dental drilling machine sounds, injections or having allergic anamnesis and anesthesia intolerance emotionally unstable or mental defectives(psychiatric disorders);
– conventional preparation of carious cavities in primary teeth with a dental drilling machine on reception at polyclinic is recommended for emotionally stable children beginning from preschool years who are tolerable to all procedure, including anesthesia;
– in the absence of good access to the carious cavity one should combine preparation techniques: to create an access to a cavity, then use sparing preparation techniques.
2. In a final stage of carious cavity preparation of primary teeth in children regardless of preparation method, one should use caries-detector to evaluate the quality of infected dentin filling. Absence of bright dentin staining is the mean of termination of carious cavity preparation of primary teeth.
3. Treating median caries in primary teeth in children aged 1-5 one should perform deep dentin fluoridation of carious cavities with sealant liquid that enhances effectiveness of treatment.
4. In children aged 1-5 to enhance effectiveness of median caries treatment of primary teeth one should use a comprehensive treatment schedule, including sparing preparations (ART and CMP) and caries – detector use, deep fluoridation of carious cavities and glass ionomer cement filling.
Publications on the thesis
1. Mohammad D.J. Practical application of chemical – mechanic preparation technique to primary teeth in children E.E.Maslak, D.J. Mohammad Actual problems of dentistry: Materials of scientific practical conference of dentists inTatarstan devoted to 50 anniversary of dental department of KSMU.-Kasany. -2004.-p.60-63.
2. Mohammad D.J. Caries – detector application to primary teeth in carious cavity preparation D.J. Mohammad, N.V. Kuyumdzhidi\ Actual problems of experimental, clinical, and preventive dentistry. – Volgograd.-2005. – volume 62, -iss.2.-p.163-165.
3. Mohammad D.J. Enhancement of caries treatment of primary teeth in children aged 1-5. D.J. Mohammad, N.N. Klimova\ X regional scientific conference of young researches in Volgograd region.- Volgograd.- 2005.- p.107-108.
4. Mohammad D.J. Comprehensive carries treatment of primary teeth. E.E.Maslak, D.J. Mohammad, F.S. Atanasova, N.V. Kuyumdzhidi \ Materials of VI international scientific practical conference “Health and education in XXI century”.- M.-2005.- p.328.
5. Mohammad D.J.Esthetic caries treatment of primary teeth in children aged 1-5 E.E.Maslak, D.J. Mohammad, F.S. Atanasova, N.V. Rozhdestvenskaya \ New technologies in medicine (morphological, experimental, clinical and social aspects): Issue of VolGMU.- Volgograd.- 2005.-iss.I.- p.383-385.
6. Mohammad D.J. Comprehensive carries treatment of primary teeth. E.E.Maslak, D.J. Mohammad, N.V. Kuyumdzhidi, F.S. Atanasova, .A.Lavrov \ Institute of dentistry.-2005.№4.-p.71.
7. Mohammad D.J. Experimental use of national glass ionomer cements ‘argcem” in caries treatment of primary teeth\ E.E.Maslak, N.N. Klimova, N.V. Kuyumdzhidi , D.J. Mohammad\ Actual problems of dentistry: Materials of interregional scientific practical conference devoted to 100- anniversary of Saratov odontologic society establishment.- Saratov-2005.-p.186-188.
8. Mohammad D.J. Children’s and parents’ attitude to different carious cavity preparation techniques of primary teeth E.E.Maslak, D.J. Mohammad, F.S. Atanasova, N.V. Kuyumdzhidi\ Actual problems of experimental, clinical, and preventive dentistry: Materials of scientific practical conference devoted to45- anniversary of dentistry department of VolSMU . – Volgograd.-2006. –p.163-165.
List of abbreviations
ART –atraumatic restorative treatment
VolSMU– Volgograd State Medical University
DF– deep fluoridation
CCDP– children clinical dentistry policlinic
GIC– glass ionomer cement
CP – conventional preparation
CM– chemical- mechanic
CMP– chemical- mechanic preparation
by Dr. Dina Jafar Mohammad