Background
The relationship of apical periodontitis (AP) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
is poorly studied in large populations. The aims of this study were to determine if
there is an independent association between AP and T2DM in a large hospital network
after controlling for confounding variables, as well as to determine if glycated hemoglobin
levels were independently associated with AP.
Methods
An initial search of the Carolina Data Warehouse for Health yielded 5,995,011 patients,
of whom 7,749 were diagnosed with AP in 2015 through 2018. Patients’ demographics,
T2DM status, HbA1c, periodontal disease, oral cellulitis, hypertension, atherosclerosis, kidney disease,
smoking, body mass index, the use of metformin or statins, and hospital inpatient
status were collected from their most recent visit. A control group of 7,749 patients
without AP were sampled and matched according to the age, race, and sex of each patient
with AP. Multiple logistic regression was used to determine the association between
T2DM and AP, as well as between HbA1c and AP after controlling for the effects of the aforementioned confounding variables,
using a matched cohort design.
Results
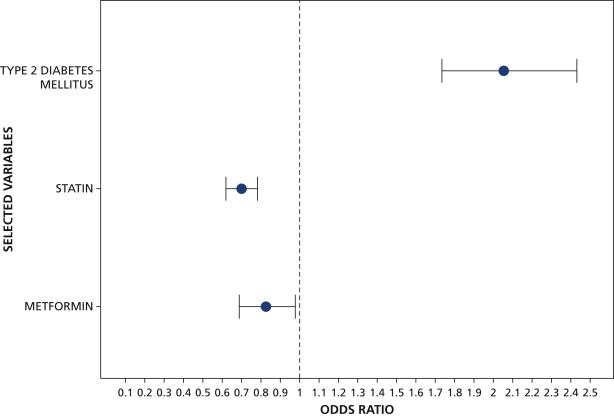
T2DM was independently associated with significantly greater prevalence of AP (odds
ratio [OR], 2.05; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.73 to 2.43). The use of metformin
(OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.98) or statins (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.78) was independently
associated with significantly lower prevalence of AP. HbA1c greater than 8.0 (OR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.83 to 3.35) was significantly associated with
greater prevalence of AP.
Conclusions
T2DM and poorly controlled glycemia were significantly associated with AP. Metformin
and statin use were associated with lower prevalence of AP.
Practical Implications
This study provides evidence linking T2DM and the level of glycemia to the increased
prevalence of AP. Statins and metformin use may be protective in this relationship.